Cross regulator is provided to control the supplies passing down the parent channel. This video is about the Head regulator and cross regulator explained by Professor Dr.

1 Typical Lay Out Of A Cross Regulator And An Offtaking Secondary Canal Download Scientific Diagram
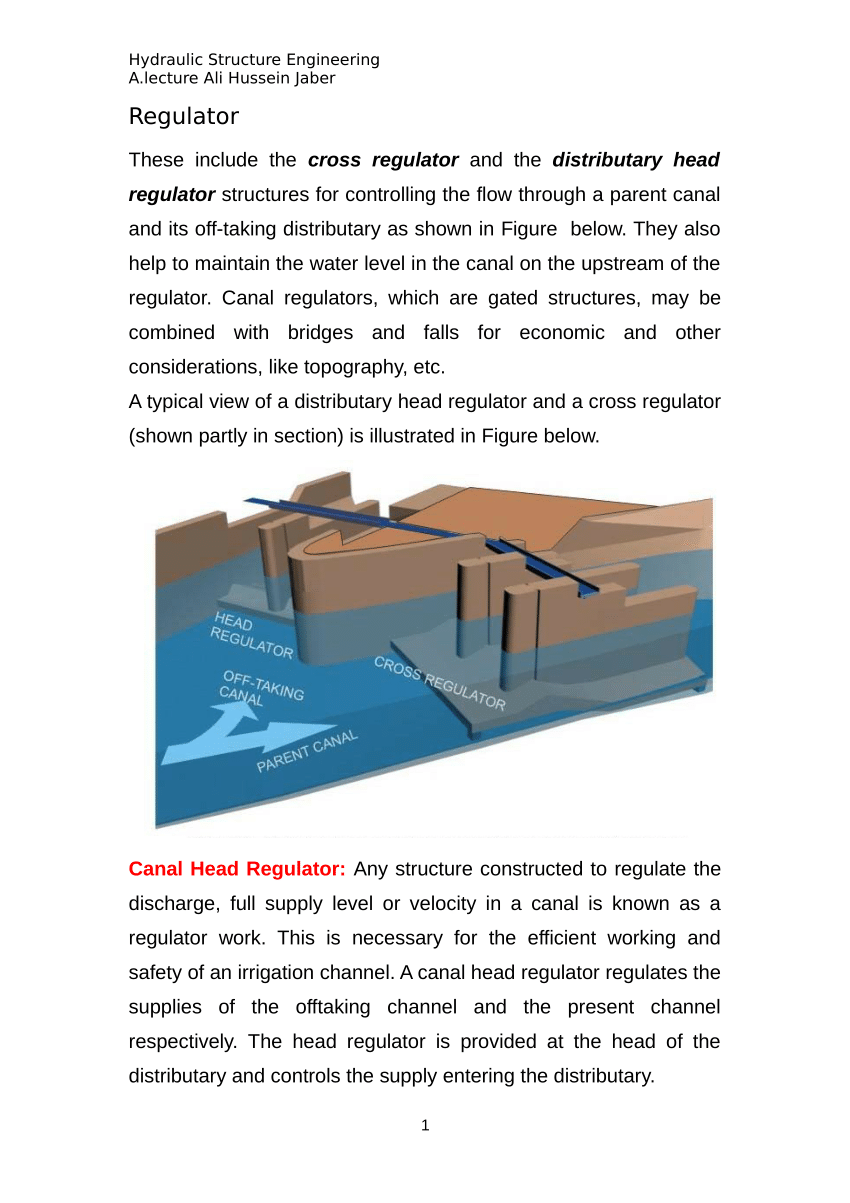
Functions of Distributary Head Regulator.
. Discharge of the distributary 15 cumecs. Some times from economic considerations the canal section is flumed at the regulator site to reduce width of the. The cross- regulator may be flumed at the site.
Adjuncts to this standard. I The crest level of the head regulator should be fixed higher than the crest of the under-sluices of the barrage with or without the silt excluder by 125 to 2 m to avoid silt entry into the canal. Ii The crest level and the waterway required by the head regulator are interrelated because the.
Adjuncts to this standard. The crest of a cross regulator is generally kept at the upstream bed level of the channel. 03 This standard covers the criteria for hydraulic design and important.
It is similar in construction to the head regulator. Ii The crest level and the waterway required by the head regulator are interrelated because the. I The crest level of the head regulator should be fixed higher than the crest of the under-sluices of the barrage with or without the silt excluder by 125 to 2 m to avoid silt entry into the canal.
I Crest level of the cross regulator should generally be kept in level with the upstream bed level of the canal. A cross-regulator is often combined with rail or a road bridge. It is a masonry or concrete structure constructed across the parent channel just Down stream of the head-regulator of the off- taking canal.
Scribd is the worlds largest social reading and publishing site. A cross regulator is provided on the parent channel at the ds of the offtake to head up the parent channel at the channel to draw the required supply. It shows the earth and construction works.
A regulator provided on the main channel at the downstream of the offtake to head up the water level and to enable the off-taking channel to draw the required supply is called a. When a fall is available on the canal the cross regulator is constructed as a fall-regulator Fig. Cross regulator and distributary head regulator are provided to control the supplies passing down the parent channel and the offtaking channel respectively.
A cross regulator is provided on the parent channel at the ds of the offtake to head up the parent channel at the channel to draw the required supply. Up to 24 cash back 135. Design a cross regulator and a head regulator for the distributary channel taking off from the parent channel for the following data.
The distributary head regulator is constructed at the upstream end ie the head of a channel where it takes off from the main canal or a branch canal or a major dis-tributaryThe distributary head regulator should be distinguished from the canal head regulator which is provided at the canal headworks where a canal takes its supplies from a river source. Its main function is to raise the water level the parent channel to such a level that requisite supplies the off-taking canal may be diverted through the head regulator. Discharge of the parent channel 100 cumecs.
Discharge of the parent canal140 cumecsvariable Discharge of distributary15 cumecsvariable Bed width of channel us52mvariable Bed width of parent channelds46mvariable Silt factor08mvariable Safe exit gradient15Assume Depth of. These include the cross regulator and the distributary head regulator structures for controlling the flow through a parent canal and its off-taking distributary as shown in Figure 123. Full supply level of parent channel us 2081 m.
Cross Regulator and Head Regulator Design - Free download as Excel Spreadsheet xls xlsx PDF File pdf Text File txt or read online for free. Read this article to learn about the twelve design principles for cross regulator and distributary head regulators. Design a cross regulator and a head regulator for a channel which takes off from parent channel.
Here we detail about the fourteen important design principles for head regulators. 2 REFERENCES Layout of canal head regulator in case of head- The Indian Standards listed below are necessary works with sediment excluder is given in Fig. Design of Cross Regulator and Distributary Hêad Regulator Crest Levels.
2 REFERENCES Layout of canal head regulator in case of head- The Indian Standards listed below are necessary works with sediment excluder is given in Fig. They also help to maintain the water. A typical layout of the canal head regulator is given in Fig.
A typical layout of the canal head regulator is given in Fig. The structural design of the cross regulator has to be closely co-ordinated with that of the head regulator of offtake when built in conjunction with the same. It is a hydraulic structure constructed at the head of.
Full supply level of parent channel Ds 20790 m. This is an engineering drawing of a head regulator of a branch canal from the main canal. Sunil Kute SirSite location is the Nashik Left Bank Canalnear MERIMa.
Cannot be used alone. While the crest level of the distributary head regulator is generally kept 03 to 10 m higher than the crest level of the cross regulator. Here we detail about the fourteen important design principles for head regulators.

Head And Cross Regulators Pdf Canal Continuum Mechanics
Solved Why Is It Required To Provide A Cross Regulator On The Main

Head And Cross Regulators Pdf Soft Matter Civil Engineering
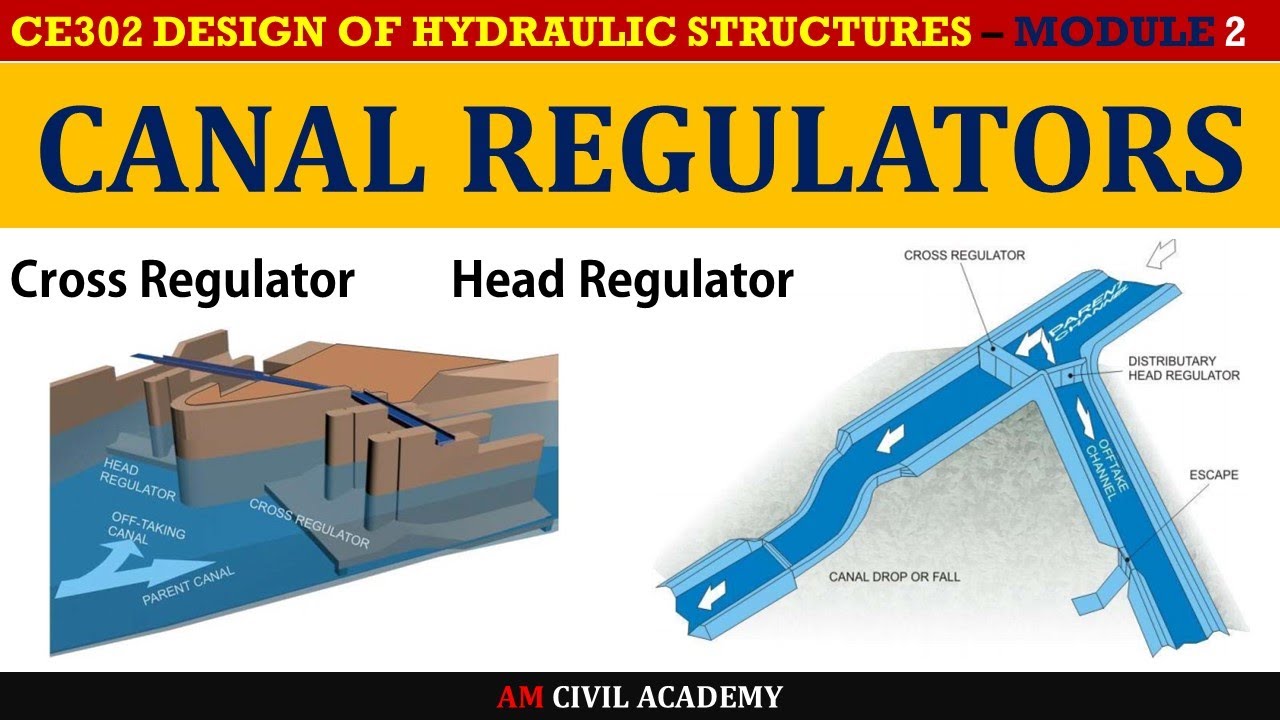
Dhs Module2 Canal Regulators Head Regulator And Cross Regulator Youtube

0 comments
Post a Comment